
Mechanical Simulation
In order for the mechanical system to run smoothly, all components and drive assemblies need to work in perfect balance.
Fewer prototypes through simulation
Vibratory mechanical assemblies can be found in many plants and machines. CAE engineers analyze and calculate not only vibrational behavior from periodic excitation, but also the impact-induced dynamic behavior of mechanical sub-systems, bearing forces and the functional reliability of the design. To keep it all manageable and economical, computer software for simulating mechanical systems is the way to go.

Simulation and analysis of mechanical components
Mechanical components must meet the highest safety and efficiency requirements, while remaining inexpensive to produce. In addition to drive technology, there are plenty of other applications fields where mechanical systems play a crucial role, such as:
-
Steering gear
-
Running gear of vehicles and landing gear of aircrafts
-
Bowden cable systems
-
Belt drives and hoisting gear (e.g. in cranes and conveyors)
-
Closing and locking mechanisms (e.g. doors, trunks, etc.)
-
Kinematics (e.g. in excavator arms)
-
Mechanisms in agricultural and textile machinery (e.g. coupled gear and disk cam mechanisms)


They consist of different mechanical elements:
-
Shafts and axes
-
Toothed gearing, coupled gear and disk cam mechanisms
-
Bowden cables
-
Elastic structures
-
Joints and couplings
-
Spring and vibration dampers
In many cases, mechanical assemblies are driven by electric motors as well as hydraulic and pneumatic actuators.
To guarantee the desired mechanical functions, all components and their drive must be perfectly adjusted to one another. For this purpose, it is indispensable to check for excitations in the drive system and for resonances in the mechanical system. That is why CAE engineers analyze a number of properties, such as fatigue and the influence of friction on each of the assemblies and on the system as whole. Determining loads, peak loads and friction losses through mechanical simulation provides a reliable basis for the selection of appropriate drives and actuators and allows for conclusions on how to dimension the individual mechanical components


Mechanical simulation for better performance of stationary and mobile machinery
Higher speed and better precision of stationary and mobile machines cannot be achieved by simply increasing the drive’s power. Higher power ratings must also meet safety and reliability standards. So it is necessary to analyze what impact high-performance powertrains may have on connected mechanical assemblies. Due to resonant frequencies and combined loads, the resulting forces may grow disproportionately in bearings, for example, despite the same design. A simulation reveals problematic load cases at an early stage and provides information on acting forces. On this basis, you can make appropriate design improvements and check their effects directly in the model.


Complex movements under control with mechanical simulation
Whether for extending or retracting a plane’s landing gear, or for robotic arms or processing operations in assembly lines – elaborate mechanics allow for highly complex movements in very confined spaces. The more complex the movement is, the more sophisticated the design becomes and the more difficult it is to determine the transmission ratio of forces and torques. A simulation model enables you to try and test your design ideas with ease: fast, inexpensive and free of risk. Sensitivity analyses using a system model help identify the parameters with the largest impact on an assembly’s properties. Automated variant calculations allow you to quickly and conveniently find the most appropriate configuration.
Learn more about simulating cables, belts, pulleys and ropes
Speed up your development in automotive engineering through mechanical simulation
In the automotive industry, OEMs expect the highest quality for supplied components. Simulation and virtual testing in vehicle development ensure proper functionality of your systems.
Optimized driving comfort
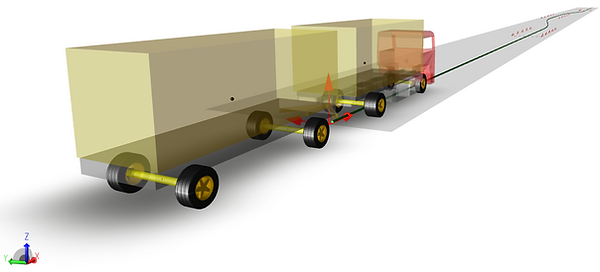
Besides reliability and safety, the vehicle’s comfort is an important criterion for a customer's purchase decision. Driving comfort and safe performance are largely influenced by the chassis’ damping properties. Vibrations from the engine and powertrain as well as road shocks are transmitted through the chassis and engine gearbox mounting into the passenger compartment. The wheel-ground contact is heavily influenced by the chassis. You can simulate and optimize vehicle driving comfort on the basis of a system model comprising the powertrain as well as the elastic and damping properties of the wheel suspension and engine mount.


Early functionality at minimum cost
Bowden cables as used in engine hoods, doors and tailgates can be excited by vibrations in the car body and come into contact with adjacent parts and thus cause rattling noises. A virtual model allows you to simulate the motion of a vibrating Bowden cable as well as the force required for actuation. These results will help you ensure the desired functionality at minimum costs, especially in high-volume production.
Significant reduction in physical prototyping needs
The mechanisms of a drum brake with automatic adjuster must work reliably both in forward and reverse gear and as a parking brake even under temperature changes. If the mechanical simulation model includes the temperature-dependent mechanical properties, you can use them to analyze the impact of design parameters on the braking behavior under varying ambient conditions. This reduces the amount of prototype testing considerably.

Automated determination of design parameters
In a power window, the mechanical parts, the geared servomotor and the control system work hand in hand. Besides reliable operation, it is important to guarantee its safety through an auto-reverse system. A software for system simulation is used not only for verifying the design in the development phase, but also for optimizing the design. Optimization algorithms help you find the best design parameters in an automated way.

Exclusive inside knowledge within the SimulationX Community
Over 700 customers worldwide rely on SimulationX as their multiphysics modeling tool to simulate and optimize fluid power components and systems.

